Edaphic factors affecting the vertical distribution of radionuclides in the different soil types of Belgrade, Serbia
Abstract
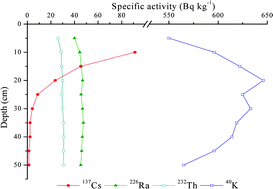
The specific activities of natural radionuclides (40K, 226Ra and 232Th) and Chernobyl-derived 137Cs were measured in soil profiles representing typical soil types of Belgrade (Serbia): chernozems, fluvisols, humic gleysols, eutric cambisols, vertisols and gleyic fluvisols. The influence of soil properties and content of stable elements on radionuclide distribution down the soil profiles (at 5 cm intervals up to 50 cm depth) was analysed. Correlation analysis identified associations of 40K, 226Ra and 137Cs with fine-grained soil fractions. Significant positive correlations were found between 137Cs specific activity and both organic matter content and

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...