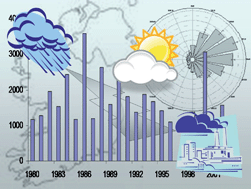
A major Irish study, based upon more than 8000 samples collected over the measurement period of 22 years, for sulfur dioxide (SO2–S), sulfate (SO4–S) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2–N) concentrations (μg m−3) within air, and the ionic composition of precipitation samples based on sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), magnesium (Mg2+), calcium (Ca2+), chloride (Cl−), sulfate (SO4–S), non-sea salt sulfate (nssSO4–S), ammonium (NH4–N), and nitrate (NO3–N) weighted mean concentrations (mg l−1), has been completed. For the air samples, the sulfur dioxide and sulfate concentrations decreased over the sampling period (1980–2004) by 75% and 45%, respectively, whereas no significant trend was observed for nitrogen dioxide. The highest concentrations for sulfur dioxide, sulfate and nitrogen dioxide were associated with wind originating from the easterly and northeasterly directions i.e. those influenced by Irish and European sources. The lowest concentrations were associated with the westerly directions i.e. for air masses originating in the North Atlantic region. This was further verified with the use of backward (back) trajectory analysis, which allowed tracing the movement of air parcels using the European Centre for Medium range Weather Forecasting (ECMWF) ERA-40 re-analysis data. High non-sea salt sulfate levels were being associated with air masses originating from Europe (easterlies) with lower levels from the Atlantic (westerlies). With the precipitation data, analysis of the non-sea salt sulfate concentrations showed a decrease by 47% since the measurements commenced.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...