Models for the adsorption of organic compounds at gas–water interfaces†
Abstract
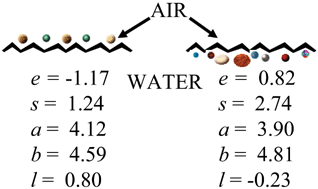
The solvation parameter model is used to characterize interactions responsible for adsorption at the gas–water interface for bulk water at 15 and 25 °C, snow at −6.8 °C, mineral-supported water films (alumina, calcium carbonate and quartz) at 15 °C, and dry soil at 15 °C. The mineral-supported water films and dry soil adsorption data are modeled at different relative humidities in the range 40–99%. The models produce satisfactory results with standard errors of the estimate of 0.12 to 0.17 for regression of the model predicted adsorption equilibrium constants against the experimental values (range for equilibrium constants −2 to −7 log units). The water surface is polar with a significant capacity for dipole-type and hydrogen-bonding interactions. In addition, it is strongly electron lone pair repulsive. Dispersion interactions favor adsorption at the water surface. Mineral-supported water films at relative humidities greater than 40% demonstrate adsorption properties similar to bulk water. The adsorption characteristics, however, depend on the relative humidity and the nature of the support. In the case of dry soil the adsorption properties at different relative humidities cannot simply be explained by adsorption of a water film covering the soil surface and the changes in adsorption characteristics with relative humidity are more complex than the mineral-supported water films.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...