High thermoelectric performance in Bi0.46Sb1.54Te3 nanostructured with ZnTe†
Abstract
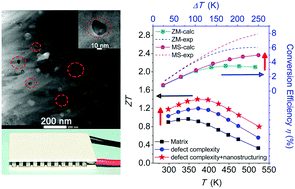
Defect engineering and nano-structuring are the core stratagems for improving thermoelectric properties. In bismuth telluride alloys nanosizing individual crystallites has been extensively studied in efforts to reduce the thermal conductivity, but nanostructuring with second phases has been more challenging. In this study, we demonstrate a thermoelectric figure of merit ZT of 1.4 at 400 K, realized in Zn-containing BiSbTe alloys (specifically Bi0.46Sb1.54Te3) by integrating defect complexity with nanostructuring. We have succeeded in creating nanostructured BiSbTe alloys containing ZnTe nanoprecipitates. We present a melt-spinning-based synthesis that forms in situ ZnTe nanoprecipitates to produce an extremely low lattice thermal conductivity of ∼0.35 W m−1 K−1 at 400 K, approaching the amorphous limit in the Bi2−xSbxTe3 system, while preserving the high power factor of Bi0.46Sb1.54Te3. These samples show excellent repeatability and thermal stability at temperatures up to 523 K. DFT calculations and experimental results show that Zn is inclined to form dual site defects, including two substitutional defects ZnBi/Sb′ and a Te vacancy, to achieve full charge compensation, which was further explicitly corroborated by Positron annihilation measurement. The strong enhancement of thermoelectric properties was validated in a thermoelectric module fabricated with the melt-spun p-legs (ZnTe-nanostructured BiSbTe) and zone-melt n-legs (conventional BiTeSe) which achieved a thermoelectric conversion efficiency of 5.0% when subjected to a temperature gradient of 250 K, representing about 40% improvement compared with a commercial zone-melt-based module. The results presented here represent a significant step forward for applications in thermoelectric power generation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
