A scanning probe investigation of the role of surface motifs in the behavior of p-WSe2 photocathodes†
Abstract
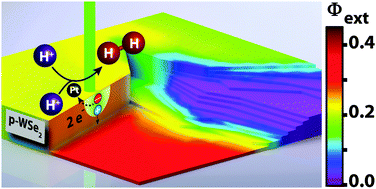
The spatial variation in the photoelectrochemical performance for the reduction of an aqueous one-electron redox couple, Ru(NH3)63+/2+, and for the evolution of H2(g) from 0.5 M H2SO4(aq) at the surface of bare or Pt-decorated p-type WSe2 photocathodes has been investigated in situ using scanning photocurrent microscopy (SPCM). The measurements revealed significant differences in the charge-collection performance (quantified by the values of external quantum yields, Φext) on various macroscopic terraces. Local spectral response measurements indicated a variation in the local electronic structure among the terraces, which was consistent with a non-uniform spatial distribution of sub-band-gap states within the crystals. The photoconversion efficiencies of Pt-decorated p-WSe2 photocathodes were greater for the evolution of H2(g) from 0.5 M H2SO4 than for the reduction of Ru(NH3)63+/2+, and terraces that exhibited relatively low values of Φext for the reduction of Ru(NH3)63+/2+ could in some cases yield values of Φext for the evolution of H2(g) comparable to the values of Φext yielded by the highest-performing terraces. Although the spatial resolution of the techniques used in this work frequently did not result in observation of the effect of edge sites on photocurrent efficiency, some edge effects were observed in the measurements; however the observed edge effects differed among edges, and did not appear to determine the performance of the electrodes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...