Multiple-bandgap vertical-junction architectures for ultra-efficient concentrator solar cells
Abstract
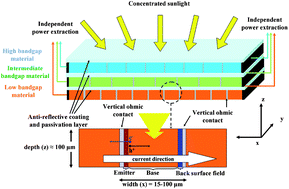
A novel multiple-bandgap multi-terminal vertical-junction (side-illumination) architecture for concentrator solar cells is proposed and simulated, wherein each stacked sub-cell operates at its own maximum power point, without the need for tunnel diodes, current matching, lattice matching,

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...