Molten catalytic coal gasification with in situ carbon and sulphur capture
Abstract
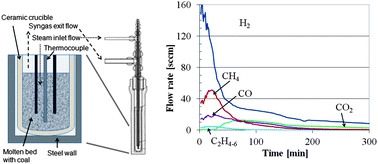
A molten catalytic process has been demonstrated for converting coal into a synthesis gas consisting of roughly 20% methane and 80% hydrogen using alkali hydroxides as both catalysts and in situ CO2 capture agents. Baselines studies were also conducted using no catalyst, weak capture agents (CaSiO3) and strong in situ capture agent for acid gases (CaO). While a similar gas composition can be achieved using CaO rather than alkali hydroxides, the rate of syngas production is greater when using molten alkali hydroxides than when using CaO as the in situ capture agent for acid gases, such as HCl, H2S and CO2. Parametric studies were conducted to understand the effects of temperature, pressure, catalyst composition, steam flow rate and the ratio of coal to alkali hydroxide on the performance of the molten catalytic gasifier in terms of kinetics and syngas composition. To measure the amount and the rate of coal conversion, we have developed a method for quantifying the coal conversion as the reduction charge remaining, which is related to the chemical oxygen demand remaining in the coal. At temperatures between 800 °C and 900 °C, we measured first-order steam-coal gasification rates using sub-bituminous coal of 2 h−1 in a fixed bed reactor while capturing significant quantities of both H2S and CO2, and while also generating 20% methane plus ethane in the syngas on a dry volume basis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...