Enhancing CO2 bio-mitigation by genetic engineering of cyanobacteria†
Abstract
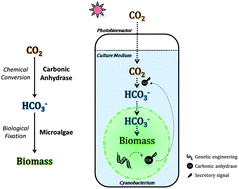
The increasing of atmospheric CO2, which is considered as a major greenhouse gas, plays a crucial role in global warming and climate change. In addition to reducing CO2 emissions from anthropogenic activities, it is more urgent to actively remove CO2 from the air. Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is a feasible but high-cost technology to remove CO2 from the flue gases of coal-fired power plants. On the other hand, CO2 sequestration by biological approaches shows potential and has the benefit that the biomass generated from the fixed CO2 can then be utilized for other purposes. However, CO2 bio-mitigation technology is still under development because the efficiency of CO2 capture and fixation is too low to be applicable in industry. In this study, we enhanced a photobioreactor-based microalgal CO2 mitigation system by combining the chemical capture/transformation of CO2 by carbonic anhydrase (CA) with the biological fixation of captured CO2 by cyanobacteria. We genetically engineered the cyanobacteria to produce and secrete CAs in the medium. The secreted CAs efficiently transformed dissolved CO2 to HCO3−. And HCO3− was taken up by the cyanobacteria and further fixed into biomass through photosynthesis. To our knowledge, we have demonstrated for the first time that CO2 can be sequestrated in a sustainable way through combining the chemical transformation of CO2 with the biological CO2 fixation in a microalgal photobioreactor system.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...