Monitoring surface transformations of metal carbodiimide water oxidation catalysts by operando XAS and Raman spectroscopy†
Abstract
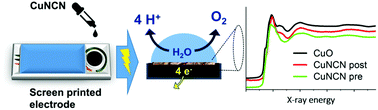
Transition metal carbodiimides MNCN (M = Co, Ni, Co0.9Ni0.1, Mn and Cu), were studied by simultaneous operando Raman and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) with focus on surface oxide detection during electrocatalytic water oxidation. As a proof of concept, easily modifiable screen-printed electrodes were used in this unified operando synchrotron setup for a trade-off between convenience of electrochemical anodization and spectroscopic data acquisition. Monitoring of chemical and structural transformations at the electrode surface during initial anodic electrode polarization shows stability for MNCN with M = Co, Ni, Co0.9Ni0.1 and Mn. While MnNCN is inactive, CoNCN emerges as the most active representative of the series. CuNCN displays pronounced side reactions and the formation of a surface copper oxide layer leading to lower current density attributed to water oxidation, as evident from an irreversible variation of the CuNCN redox behaviour in rotating ring-disc voltammetry. Furthermore, the accompanying structural and vibrational spectroscopy properties of the different MNCN compounds were explored with complementary ex situ analytical methods.
- This article is part of the themed collection: New Talent: Europe


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...