The role of l-cysteine and introduced surface defects in reactive oxygen species generation by ZnO nanoparticles†
Abstract
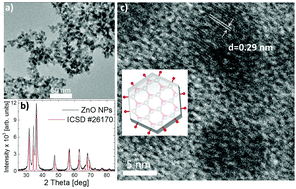
The synthesis and surface functionalization of ZnO nanoparticles were performed, with attention being paid to the possible bio-related applications in light-triggered reactive oxygen species generation. L-Cysteine molecules possessing sulfur atoms with high affinity to the ZnO surface proved to be interesting ligands, providing the improvement of the colloidal stability of the nanoparticles in aqueous solutions, and enhancing the efficiency of reactive oxygen species generation for antibacterial and photodynamic-based cancer treatment applications. Depending on the amount of the sulfur-containing ligands available for bonding to the ZnO nanoparticles, the ion exchange process occurring at the ZnO surface was observed. Both the experimental measurements and numerical calculations, performed in the frame of density functional theory, showed that the surface adhered OH− and SH− groups play a dominant role in the formation of the reactive oxygen species in the presence of ZnO nanoparticles in solution upon ultraviolet and blue light excitation. It was also observed that the efficiency of the reactive oxygen species generation process may also be enhanced by the adhesion of the SH− groups onto the surface of the ZnO clusters.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...