Chlorinated cobalt alkyne complexes derived from acetylsalicylic acid as new specific antitumor agents†
Abstract
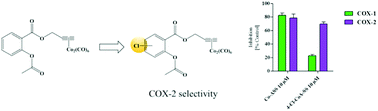
[(Prop-2-ynyl)-2-acetoxybenzoate]dicobalthexacarbonyl (Co-ASS), an organometallic derivative of the irreversible cyclooxygenase-1/2 (COX-1/2) inhibitor acetylsalicylic acid (ASS), demonstrated high growth-inhibitory potential against various tumor cell lines and inhibition of both COX isoenzymes. With the objective of increasing the selectivity for COX-2, we introduced a chlorine substituent in position 3, 4, 5, or 6 of the ASS moiety, respectively. Increased COX-2 selectivity is desirable as this isoenzyme is predominantly related to the development of cancer and abnormal tissue growth. The new compounds were investigated in comprehensive cellular biological assays to identify the impact of the chlorine substitution at the complex on COX-1/2 inhibition, antiproliferative activity, apoptosis, metabolic activity, cell-based COX inhibition, and cellular uptake. Chlorination distinctly reduced the effects at isolated COX-1 (about 25% inhibition at 10 μM; Co-ASS: 82.7%), while those at COX-2 remained almost unchanged (about 65% inhibition at 10 μM; Co-ASS: 78.5%). In cellular systems, with exception of the 6-Cl derivative, all compounds showed notable antitumor activity in COX-1/2 expressing tumor cells (HT-29 (IC50 = 1.5–2.7 μM), MDA-MB-231 (IC50 = 5.2–8.0 μM)), but were distinctly less active in the COX-1/2-negative MCF-7 breast cancer cell line (IC50 = 15.2–22.9 μM). All complexes possess high selectivity for tumor cells, because they did not influence the growth of the non-tumorigenic, human bone marrow stromal cell line HS-5. These findings clearly demonstrate that the interference with the COX-1/2 cascade contributes to the mode of anticancer action of the cobalt alkyne complexes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...