Insights into disilylation and distannation: sequence influence and ligand/steric effects on Pd-catalyzed difunctionalization of carbenes†
Abstract
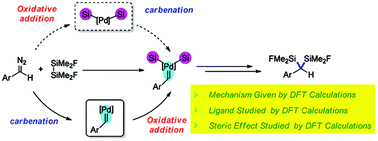
Density functional theory (DFT) calculation has been used to reveal the mechanism of Pd-catalyzed disilylation of carbene, which is a pathway to construct disilylmethane derivatives. The DFT calculations indicate that the reaction starts with carbenation of a Pd(0) catalyst. Oxidative addition of disilane can then generate a carbene-coordinated disilylpalladium intermediate. Carbene insertion into the Pd–Si bond followed by reductive elimination gives the disilylmethane product and regenerates the Pd(0) catalyst with the formation of two C–Si bonds. The rate-determining step of this reaction is the carbenation step. The computational results show that the phosphine ligand is unfavorable for this type of reaction because of its high dissociation energy. In this type of reaction, a smaller substrate is favorable for the oxidative addition step because the weaker steric repulsion leads to a lower activation free energy of the oxidative addition step. The computational results also reveal that the reactivity of digermane and distannane is higher than that of disilane, which can be attributed to their low bond dissociation energies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...