Noncovalent immobilization and surface characterization of lanthanide complexes on carbon electrodes†
Abstract
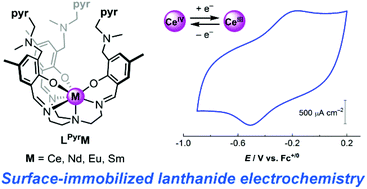
A new tripodal ligand featuring three appended pyrene moieties has been prepared for studies of noncovalent binding of lanthanide metal complexes to graphitic carbon surfaces. The ligand tightly binds lanthanide(III) ions by encapsulation within a heptadentate coordination environment; the cerium, neodymium, samarium, and europium complexes (all with formal metal oxidation state of +3) have been synthesized and characterized. These compounds are readily immobilized on graphitic electrodes—this is driven by the presence of the pyrene moieties, as complexes of an analogous ligand without pyrene groups are not stably adherent to the surface. X-ray photoelectron spectra confirm the molecular identity of the pyrene-appended metal complexes upon immobilization, with unique signals appearing for the metal centers as well as all for all symmetry-related nitrogen atoms on the ligand. Consistent with these surface characterization data and studies of a soluble model compound, the surface-immobilized cerium(III) complex is reversibly oxidized to cerium(IV) near −0.34 V vs. Fc+/0. Based on electrochemical data, this complex is stable for minutes to hours on the surface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...