Thermo-enhanced ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone: the synthesis, characterization, and catalytic behavior of aluminum hydroquinolin-8-olates†
Abstract
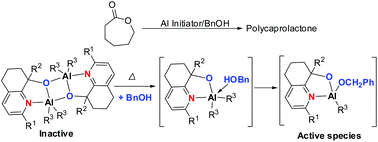
A series of highly sensitive aluminum hydroquinolin-8-olates (C1–C8) was synthesized and characterized by 1H/13C NMR spectroscopy. The molecular structures of compounds C1, C3, C4, and C5 were confirmed by single crystal X-ray crystallography and demonstrated the binuclear form. In the presence of BnOH, all the aluminum complexes exhibited moderate to high activities towards the ring-opening polymerization of ε-CL at high temperatures, but quite low activities at ambient temperature. Microstructure analysis of the resultant polycaprolactones showed that the polymers were linear in nature with a BnO− end group. In addition, the mechanism was investigated by monitoring the 1H NMR and 27Al NMR of C1 and these results suggested that the complexes existed as dimeric species at low temperature and partly converted into active mononuclear species at higher temperatures, which was easily coordinated by BnOH to afford the active species for the ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...