Intramolecular Lewis pairs with two acid sites – reactivity differences between P- and N-based systems†
Abstract
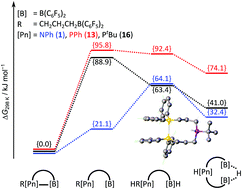
The doubly acid-functionalised aniline PhN[(CH2)3B(C6F5)2]2 shows rapidly exchanging boron acid groups at the central base function and is an active frustrated Lewis pair due to cooperative hydride binding by both Lewis acids. Here we report investigations on the effect of different substituents at the central nitrogen atom and on the effect of exchanging nitrogen by phosphorus. Treatment of diallyl-tert-butylaniline with one equivalent of HB(C6F5)2 led to formation of a seven-membered iminium hydridoborate ring; after mono-hydroboration the intermediately formed frustrated Lewis pair reacts with the second allylamine function under ring closure. Phosphorus based Lewis pairs with two acid sites were prepared by hydroboration of diallylphenylphosphane and diallyl-tert-butylphosphane. Unlike the aniline PhN[(CH2)3B(C6F5)2]2 the doubly hydroborated species (tBu/Ph)P[(CH2)3B(C6F5)2]2 show no dynamic exchange of the boron Lewis acid functions in solution and are not catalytically active in terms of H/D-scrambling as well as hydrogenation reactions. Quantum-chemical investigations revealed the B–P bond dissociation Gibbs free energy to be much larger than those of the nitrogen analogue. The absence of an active open form in solution prevents an activity in heterolytic hydrogen splitting.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...