A lipophilic copper(ii) complex as an optical probe for intracellular detection of NO†
Abstract
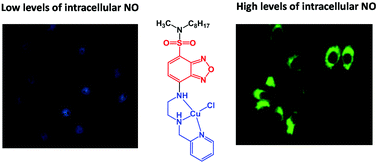
A new chemical sensor for cellular imaging of NO is presented. This cell-permeable probe is based on a complex where copper(II) is coordinated to a tridentate ligand substituted with a fluorophore (NBD) and an octyl group. The fluorescence response of this complex towards a range of reactive species (namely NO, NO2−, NO3−, H2O2, ClO−, O2− and ONOO−) has been studied in vitro showing that the probe is highly selective for NO. The probe is readily taken up by cells and is able to image the cellular concentrations of NO.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...