Stability and toxicity of tris-tolyl bismuth(v) dicarboxylates and their biological activity towards Leishmania major†
Abstract
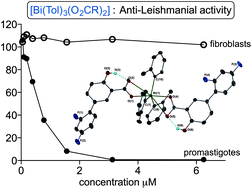
A series of 29 tris-tolyl bismuth(V) di-carboxylato complexes of composition [Bi(Tol)3(O2CR)2] involving either ortho, meta or para substituted tolyl ligands have been synthesized and characterised. Of these 15 were assessed for their toxicity towards Leishmania promastigotes and human fibroblast cells, with ten then being subsequently assessed against parasite amastigotes. The carboxylate ligands are drawn from a series of substituted and biologically relevant benzoic acids which allow a comparison with earlier studies on [BiPh3(O2CR)2] and analogous Sb(V) [SbAr3(O2CR)2] (Ar = Ph and Tol) complexes. Twelve complexes have been structurally characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction and shown to adopt a typical trigonal bipyramidal geometry in which the three tolyl ligands occupy the equatorial plane. NMR studies on two illustrative examples indicate that the complexes are stable in D2O and DMSO but only have a half-life of 1.2 hours in culture medium, with glucose being a contributing factor in decomposition and reduction to Bi(Tol)3. Despite their short lifetime many complexes show significant toxicity towards promastigotes at low concentration (<6 μM) and at that concentration provide for good selectivity indices (parasite vs. mammalian cells), for example 114 for [Bi(o-Tol)3(O2CC6H3(2-OH,5-C6H3(2,4-F2)))2] and 838 for [Bi(m-Tol)3(O2CC6H4(2-OAc))2]. Best activity and selectivity is observed with complexes containing o- and m-tolyl ligands, and it appears the primary influence on fibroblast toxicity is the Ar ligand while the carboxylate influences promastigote toxicity. The complexes are less effective in vitro against the parasite amastigotes, where longer incubation times and harsher chemical and biological environments are encountered in the assay. Nevertheless, there were some statistically relevant differences at 1 μM against the positive controls with the best performing complexes being [Bi(o-Tol)3(O2CC6H4(2-EtO))2] and [Bi(m-Tol)3(O2CC6H4(2-OAc))2].

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...