Water-soluble oxoglaucine-Y(iii), Dy(iii) complexes: in vitro and in vivo anticancer activities by triggering DNA damage, leading to S phase arrest and apoptosis†
Abstract
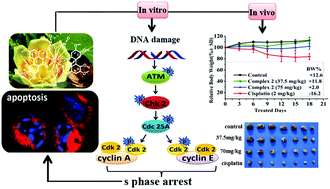
Complexes of yttrium(III) and dysprosium(III) with the traditional Chinese medicine active ingredient oxoglaucine (OG), namely [Y(OG)2(NO3)3]·CH3OH (1) and [Dy(OG)2(NO3)3]·H2O (2), were synthesized and characterized by elemental analysis, IR, ESI-MS, 1H and 13C NMR as well as single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. In vitro the complexes exhibited higher anticancer activity than the free ligand OG against the tested cancer cell lines. Among the tested cell lines, HepG2 is the most sensitive to the complexes. Complex 2 can trigger DNA damage in HepG2 cells, resulting in cell cycle arrest in the S phase and leading to cell apoptosis. The S phase cell-cycle arrest is caused via the ATM (ataxia-telangiectasia mutated)-Chk2-Cdc25A pathway. Chk2 is phosphorylated and activated in an ATM-dependent manner. It, in turn, phosphorylates Cdc25A phosphatise on serine124, causing the inactivation of Cdc25A in ubiquitin-mediated proteolytic degradation. The cyclin-Cdk complexes of the S phase could also be inhibited by limited supply of cyclins A and E. This irreversible cell cycle arrest process ultimately induces mitochondria-involved apoptotic cell death via the activation of Bcl-2 protein. Complex 2 effectively inhibited tumour growth in the BEL-7402 xenograft mouse model and exhibited higher safety in vivo than cisplatin.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...