Chemical “top-down” synthesis of amphiphilic superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanobelts from exfoliated FeOCl layers†
Abstract
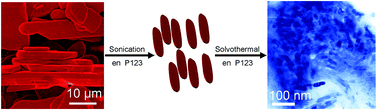
A novel chemical “top-down” method has been employed to prepare tiny Fe3O4 nanobelts. Uniform Fe3O4 nanobelts were obtained by solvothermal reduction of exfoliated FeOCl layers with the assistance of high polar solvents and a PEO–PPO–PEO stabilizer. We also studied the superparamagnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanobelts, which exhibit a magnetic saturation value as high as ∼53 emu g−1 at room temperature and a magnetic anisotropy constant up to 6.6 × 104 erg cm−3. Furthermore the as-obtained product, which is amphiphilic and exhibits excellent dispersibility and redispersibility in most of the common solvents, could be readily used in various realms of biomedicine and biotechnology.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...