Evidence of low dimensional ion transport in mechanosynthesized nanocrystalline BaMgF4
Abstract
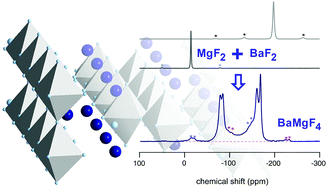
Mechanochemical milling provides a versatile method for the preparation of nano-sized, defect rich, polycrystalline materials. If ionic materials are considered, the transport parameters of the mobile ions may greatly differ from those of the microcrystalline counterparts prepared by conventional synthesis routes. Little is known about ionic conduction in nanocrystalline materials having crystal structures that offer spatially confined transport pathways. Here, we focused on mechanosynthesized BaMgF4 that combines both nanocrystallinity and anisotropic F− transport. The preparation of nanocrystalline BaMgF4 is presented as a facile and rapid one-pot procedure. The reaction was followed by X-ray diffraction and high-resolution 19F nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. NMR helped prove the formation of X-ray amorphous compounds as well as the transformation of the starting materials into the final product BaMgF4. Most importantly, besides enhanced conduction properties compared to a single crystal, our broadband impedance spectra reveal characteristics pointing to anisotropic (low dimensional) ion transport processes even in the nanocrystalline form of BaMgF4.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...