Application of hydrophobically modified water-soluble polymers for the dispersion of hydrophobic magnetic nanoparticles in aqueous media†
Abstract
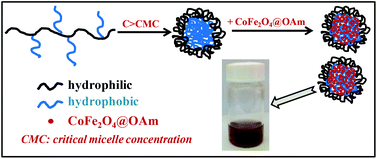
Hydrophobically modified water-soluble polymers (HMWSPs), comprised of a poly(sodium methacrylate) (PMANa) or poly(sodium acrylate) (PANa) backbone and pendent dodecyl methacrylate (DMA) or dodecyl acrylamide (DAAm) chains, respectively, were synthesized. The hydrophobic content of the copolymers, P(MANa-co-DMA) and P(ANa-co-DAAm), is in the range of 0 to 25 mol%, while their weight-average molar mass varies from ∼10 000 up to ∼75 000. Their self-assembly behavior in dilute aqueous solution was followed through Nile Red probing, DLS and TEM measurements. The critical micelle concentration (CMC) is mainly controlled by the hydrophobic content and not the molar mass of the copolymers. Above CMC, spherical and large-compound micelles are identified by DLS and TEM. Moreover, oleylamine coated CoFe2O4 nanoparticles (CoFe2O4@OAm MNPs) of 9.4 nm with a saturation magnetization Ms = 85 emu g−1 were solvothermally prepared. The hydrophobic CoFe2O4@OAm MNPs were successfully encapsulated into the hydrophobic cores of the structures formed by the copolymers above CMC through a solvent mixing procedure, and in that way hydrophilic CoFe2O4@HMWSP nanohybrids resulted. For comparison purposes, two alternate phase transfer approaches were also used to convert CoFe2O4@OAm MNPs to hydrophilic ones: (a) addition of a coating layer by cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) and (b) by the ligand exchange procedure with 2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA). NMR transverse relaxivity measurements of the aqueous suspensions of CoFe2O4@P(ANa-co-DAAm), CoFe2O4@CTAB and CoFe2O4@DMSA were recorded and the r2 relaxivity was determined. CoFe2O4@CTAB demonstrated the highest r2 relaxivity of 554.0 mM−1 s−1, while CoFe2O4@P(ANa-co-DAAm) and CoFe2O4@DMSA showed lower values of 313.6 mM−1 s−1 and 76.3 mM−1 s−1, respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...