Reducing the inversion degree of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles through synthesis to enhance magnetization: evaluation of their 1H NMR relaxation and heating efficiency†
Abstract
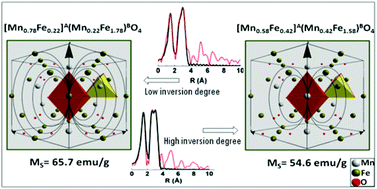
Manganese ferrite (MnFe2O4) nanoparticles of identical size (9 nm) and with different inversion degrees were synthesized under solvothermal conditions as a candidate theranostic system. In this facile approach, a long-chain amine, oleylamine, was utilized as a reducing and surface-functionalizing agent. The synthesized nanoparticles were shown to have a cubic-spinel structure as characterized by TEM and XRD patterns. Control over their inversion degree was achieved by a simple change of manganese precursor from Mn(acac)2 to Mn(acac)3. The variation in the inversion degree is ascribed to the partial oxidation of Mn2+ to Mn3+, as was evidenced by X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy and extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy at both the Fe and Mn K-edges. The reduction of the inversion degree from 0.42 to 0.22 is close to the corresponding bulk value of 0.20 and led to elevated magnetization (65.7 emu g−1), in contrast to the Néel temperature, which was decreased owing to the weaker superexchange interactions between the tetrahedral and octahedral sites within the spinel structure. In order to evaluate the performance of these nanoprobes as a possible bifunctional targeting system, the 1H NMR relaxation of the samples was tested together with their specific loss power under an alternating magnetic field as a function of concentration. The hydrophobic as prepared MnFe2O4 nanoparticles converted to hydrophilic nanoparticles with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB). The MnFe2O4 nanoparticles, well-dispersed in aqueous media, were shown to have r2 relaxivity of up to 345.5 mM−1 s−1 and heat release of up to 286 W g−1, demonstrating their potential use for bioapplications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...