Three molybdophosphates based on Strandberg-type anions and Zn(ii)-H2biim/H2O subunits: syntheses, structures and catalytic properties†
Abstract
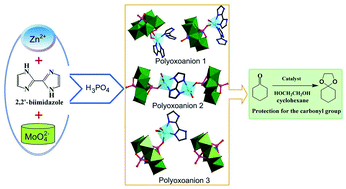
Three new inorganic–organic hybrid compounds based on Strandberg-type anions and Zn(II)-H2biim/H2O subunits, namely {H4(H2biim)3}[Zn(H2biim)(H3biim)(H2O)(HP2Mo5O23)]2·3H2O (1), {H9(H2biim)7}[(μ-biim){(Zn(H2O)2)0.5(HP2Mo5O23)}2]·7H2O (2) and {H7(H2biim)7}[Zn(H2biim)(H2O)2(HP2Mo5O23)][H2P2Mo5O23]·8H2O (3) (H2biim = 2,2′-biimidazole), have been synthesized in aqueous solutions and characterized. They were also used as efficient and reusable catalysts for the protection of carbonyl compounds. Their fascinating structural features are that mono Zn(II)-supporting biphosphopentamolybdate ({P2Mo5}) clusters exist in their crystal structures, and the nitrogen donor ligand H2biim exhibits three different coordination modes in these three compounds, respectively: for 1, two 2,2′-biimidazole molecules, as mono- and bidentate ligands coordinate to the same Zn(II) ion; for 2, one bi-negative tetradentate ligand μ-biim bridges two Zn(II) ions, while for 3, one neutral bidentate H2biim ligand links one Zn(II) ion. Most importantly, compounds 1–3 represent the first example where Strandberg-type POMs are used as acid-catalysts in an organic reaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...