Synthesis, characterisation and some chemistry of C- and B-substituted carboxylic acids of cobalt bis(dicarbollide)†
Abstract
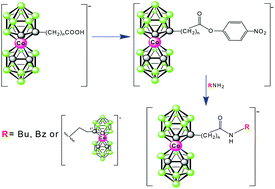
Low temperature reactions of lithiated cobalt bis(1,2-dicarbollide)(1−) (1−) in DME with carbon dioxide leads to the substitution of 1− at the C-atoms by carboxy function(s). This results in a good yield formation of monosubstituted and disubstituted products of formulations [(1-HOOC-1,2-C2B9H10)(1′,2′-C2B9H11)-3,3′-Co)]− (2−) and [(HOOC)2-(1,2-C2B9H10)2–3,3′-Co]− (3a,b−), respectively. Indeed, the latter compound is in fact a mixture of two diastereoisomers, denoted here as 1,1′-anti (3a−) and 1,2′-syn-isomer (3b−), from which only the former major species (3a−) could be isolated in pure form. Considerations about stereochemistry of these species are supported by geometry optimizations and calculations of 11B NMR shifts at the GIAO-DFT level. In addition, three monocarboxylic acids with three different linear spacers between the carboxy groups and the cage are reported. The first one of the formula [(1-HOOC-CH2-1,2-C2B9H10)(1′,2′-C2B9H11)-3,3′-Co]− (5−) results in a lithiation followed by reaction with BrCH2COOEt and hydrolysis of the respective ethyl ester (4−). Another one with ethylene chain [(1-HOOC-(CH2)2-1,2-C2B9H10)(1′,2′-C2B9H11)-3,3′-Co]− (6−) was prepared by the oxidation of a hydroxypropyl derivative of the ion 1−. The sole representative of B-substituted species of the formulation [8-(HOOC-CH2-O-1,2-C2B9H10)(1′,2′-C2B9H11)-3,3′-Co]− (7−) is prepared by alkylation of the known 8-hydroxy derivatives of the ion 1− by BrCH2COOEt and alkaline hydrolysis. A synthetic route to active nitrofenyl esters (8−, 9− and 10−) is described here based on the respective acids 5− to 7−. As verified, the nitrophenyl esters provide easy access to the formation of amidic bonds between the boron cage and organic primary amino functions. Examples of compounds containing butylamide or benzylamide [(1-RNHOC-(CH2)n-1,2-C2B9H10)(1′,2′-C2B9H11)-3,3′-Co]− (n = 1,2; R = Bu 11a,b−, R = Bn: 12a,b−) end group are described. Also the possibility of inter-connecting two clusters of the anion 1−via the amidic bond is shown in derivative (13−). These methods are applicable in the synthesis of a variety of functional molecules, particularly those applicable in drug design, surface modifications, and material science.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Carboranes

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...