Colorimetric detection of fluoride ion by 5-arylidenebarbituric acids: dual interaction mode for fluoride ion with single receptor†
Abstract
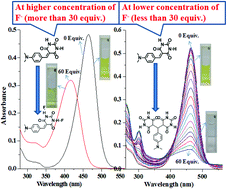
Two 5-arylidenebarbituric acid derivatives (IH and IM) have been synthesized by the Knoevenagel condensation of barbituric acid with 4-N,N-dimethylamino benzaldehyde and studied for anion sensing activities. Both receptors sense fluoride ion with high selectivity and sensitivity and the sensing action has been demonstrated by naked eye detection, UV-visible absorption, and fluorescence spectral changes in the presence of F−. Indeed, the F− sensing mechanism for receptor IH depends on F− ion concentration. While at higher concentrations F− forms strong hydrogen bonding interaction with the N–H proton of the receptor, at lower concentrations sensing is influenced by the deprotonation of the methylene proton, followed by the chemical reaction, which is also confirmed by the 1H-NMR technique. On the other hand, when replacing the N–H proton with a methyl group, IM does not show any concentration dependent behaviour with F−. The F− concentration dependent sensing is attributed to the changes in the receptor–anion interaction equilibrium, where at higher F− concentrations, F− interacts with the receptor through hydrogen bonding and at lower concentrations it induces a chemical reaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...