Mono lacunary phosphomolybdate supported on MCM-41: synthesis, characterization and solvent free aerobic oxidation of alkenes and alcohols
Abstract
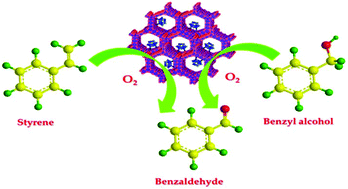
A new catalyst comprising monolacunary phosphomolybdate and MCM-41 was synthesized and characterized by different physicochemical techniques. The catalytic activity was evaluated by carrying out solvent free aerobic oxidation of alkenes and alcohols. The catalyst showed 60% conversion of styrene and 28% conversion of benzyl alcohol. The superiority of the present catalytic system lies in obtaining better conversion under solvent free and aerobic conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...