Production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species by light irradiation of a nitrosyl phthalocyanine ruthenium complex as a strategy for cancer treatment†
Abstract
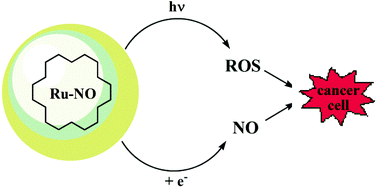
Production of reactive oxygen species has been used in clinical therapy for cancer treatment in a technique known as Photodynamic Therapy (PDT). The success of this therapy depends on oxygen concentration since hypoxia limits the formation of reactive oxygen species with consequent clinical failure of PDT. Herein, a possible synergistic effect between singlet oxygen and nitric oxide (NO) is examined since this scenario may display increased tumoricidal activity. To this end, the trinuclear species [Ru(pc)(pz)2{Ru(bpy)2(NO)}2](PF6)6(I) (pc = phthalocyanine; pz = pyrazine; bpy = bipyridine) was synthesized to be a combined NO and singlet oxygen photogenerator. Photobiological assays using (I) at 4 × 10−6 M in the B16F10 cell line result in the decrease of cell viability to 21.78 ± 0.29% of normal under light irradiation at 660 nm. However, in the dark and at the same concentration of compound (I), viability was 91.82 ± 0.37% of normal. The potential application of a system like (I) in clinical therapy against cancer may be as an upgrade to normal photodynamic therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...