Theoretical study on superalkali (Li3) in ammonia: novel alkalides with considerably large first hyperpolarizabilities†
Abstract
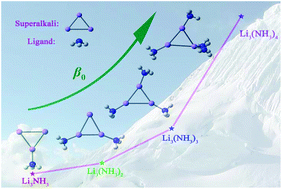
Superalkali Li3 dissolved in gaseous ammonia is investigated by density functional theory. Similar to the lithium atom, Li3 can coordinate up to four ammonia molecules. Among the structural isomers of Li3(NH3)n (n = 1–4), the one with separately distributed NH3 ligands is preferred. Most of the Li3(NH3)n species possess the alkalide characteristics and exhibit considerably large static first hyperpolarizabilities (β0) up to 3.9 × 105 au. Especially, for the lowest-energy Li3(NH3)n complexes, a prominent coordination number dependence of β0 is found as follows: 12 608 (n = 1) < 38 564 (n = 2) < 121 726 (n = 3) < 391 149 au (n = 4). In addition, the case of introducing a Na atom into such superalkali–ammonia systems has been considered and the resulting Li3(NH3)nNa (n = 1–4) complexes are studied in the same vein. It is revealed that the β0 values of Li3(NH3)nNa are influenced by both the coordination number and the relative position of NH3 ligands. We hope that this study could provide a new type of alkalides and raise the possibility of exploring a fresh, thriving area, i.e. superalkali solutions with solvents of all sorts.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...