A cap-type Schiff base acting as a fluorescence sensor for zinc(ii) and a colorimetric sensor for iron(ii), copper(ii), and zinc(ii) in aqueous media†
Abstract
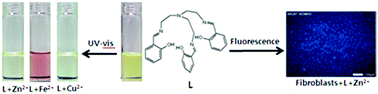
A simple and low cost chemosensor is described. This sensor could simultaneously detect three biologically important metal ions through fluorogenic (Zn2+) and chromogenic (Fe2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+) methods in aqueous solution. The sensor could function as a “turn-on” fluorescence receptor only to Zn2+ ions. In addition, the sensor could be successfully applied to the detection of intracellular Zn2+. Meanwhile, the sensor displayed an obvious red color upon selective binding with Fe2+. Therefore, the sensor could serve as a useful tool for the discrimination of Fe2+ from Fe3+ in aqueous media. Moreover, the sensor also showed color changes from yellow to colorless upon selective binding with Zn2+ and Cu2+, respectively. The detection limit of the sensor for Cu2+ (1.5 μM) is far below the guidelines of the World Health Organization (30 μM) as the maximum allowable copper concentration in drinking water, and therefore it is capable of being a practical system for the monitoring of Cu2+ concentrations in aqueous samples. These results provide a new approach for selectively recognizing the most important three trace elements in the human body simultaneously, for Zn2+ by emission spectra and Fe2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+ by the naked eye.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...