Oxa-thia-, oxa-selena and crown ether macrocyclic complexes of tin(ii) tetrafluoroborate and hexafluorophosphate – synthesis, properties and structures†
Abstract
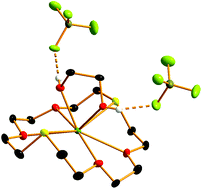
The reactions of Sn(BF4)2 and Sn(PF6)2 with crown ethers and oxa-thia- or oxa-selena-macrocycles are complex, with examples of fragmentation of the fluoroanions, and cleavage of the ligands observed, in addition to adduct formation. The reaction of Sn(BF4)2 with 15-crown-5 or 18-crown-6 produced the sandwich complex [Sn(15-crown-5)2][BF4]2 with 10-coordinate tin, and [Sn(18-crown-6)(H2O)][BF4]2·2H2O which has an hexagonal pyramidal tin centre with two long contacts to lattice water molecules (overall 7 + 2 coordination). [Sn(18-crown-6)(PF6)][PF6] is formed from 18-crown-6 and Sn(PF6)2, but the hexafluorophosphate ions hydrolyse readily in these systems to produce F− which coordinates to the tin to produce [Sn(18-crown-6)F][PF6], which can also be made directly from Sn(PF6)2, 18-crown-6 and KF in MeCN. The structure contains a hexagonal pyramidal coordinated Sn(II) cation with an apical fluoride. The oxa-thia macrocycle [18]aneO4S2 forms [Sn([18]aneO4S2)(H2O)2(PF6)][PF6], from which some crystals of composition [Sn([18]aneO4S2)(H2O)2(PF6)]2[PF6][F] were obtained. The cation contains an approximately planar O4S2 coordinated macrocycle, with two coordinated water molecules on one side of the plane and a weakly bound (κ2) PF6− group on the opposite face, and with the fluoride ion hydrogen bonded to the coordinated water molecules. In contrast, the oxa-selena macrocycle, [18]aneO4Se2, produces an anhydrous complex [Sn([18]aneO4Se2)(PF6)2] which probably contains coordinated anions, although it decomposes quite rapidly in solution, depositing elemental Se, and hence crystals for an X-ray study were not obtained. Reacting Sn(BF4)2 and [18]aneO4Se2 or [18]aneO4S2 also causes rapid decomposition, but from the latter reaction crystals of the 1,2-ethanediol complex [Sn([18]aneO4S2){C2H4(OH)2}][BF4]2 were isolated. The structure reveals the coordinated macrocycle and a chelating diol, with the O–H protons of the latter hydrogen bonded to the [BF4]− anions. This is a very rare, structurally authenticated example of ring opening/cleavage of an oxa-thia macrocycle. The new complexes were characterised by microanalysis, IR, 1H, 19F{1H} and 31P{1H} NMR spectroscopy as appropriate, and X-ray structures are reported for [Sn(15-crown-5)2][BF4]3[H3O]·H2O, [Sn(18-crown-6)(H2O)][BF4]2·2H2O, [Sn(18-crown-6)F][PF6], [Sn([18]aneO4S2)(H2O)2(PF6)]2[PF6][F] and [Sn([18]aneO4S2){C2H4(OH)2}][BF4]2. The complexes are compared and contrasted with chloro-tin(II) complexes of crown ethers, germanium(II) and lead(II) analogues.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...