Hydration of the calcium(ii) ion in an aqueous solution of common anions (ClO4−, Cl−, Br−, and NO3−)†
Abstract
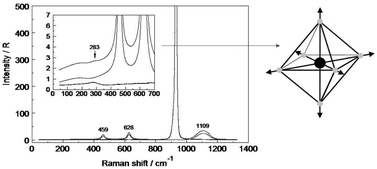
Raman spectra of aqueous calcium salt solutions, Ca(ClO4)2, CaCl2, CaBr2, and Ca(NO3)2, were measured from the concentrated solution stage to more dilute solutions (6.08–0.1 mol L−1) at 23 °C in water and heavy water down to 40 cm−1. In aqueous Ca(ClO4)2 solutions a strongly polarized band at 283 cm−1 (full width at half height (fwhh) = 68 cm−1) was observed. The mode at 283 cm−1 was assigned to the Ca–O symmetric stretching vibration of the hexa-aqua Ca2+ ion, [Ca(OH2)6]2+, and the integrated band intensity showed a linear dependency with Ca(ClO4)2 concentration. In a Ca(ClO4)2 solution of heavy water a similar band was observed at 268 cm−1 (fwhh = 64 cm−1) of the deuterated species, [Ca(OD2)6]2+. In the OH stretching region of water a band of weakly H-bonded O–H oscillators was detected at 3550 cm−1 due to O–H⋯ClO4−. In D2O solutions a similar band was found at 2590 cm−1 due to O–D⋯ClO4−. The band at 283 cm−1, in addition to the restricted translation mode of water at ∼180 cm−1, was also observed in dilute to moderately concentrated CaCl2 and CaBr2 solutions. This fact is strong evidence that neither Cl− nor Br− penetrate the first hydration sphere of Ca2+ in solution with mol ratio H2O : CaCl2/CaBr2 ≥ 18 : 1 and the coordination number is unchanged. Furthermore, the influence of CaCl2 on the water bands of the librational band region (300–900 cm−1), the deformation band of water and the O–H stretching region has been described. In a hydrate melt and very concentrated solutions of CaCl2 with a mol ratio H2O : CaCl2 ≤ 9 : 1, however, contact ion pairs between Ca2+ and Cl− are formed and the 283 cm−1 band vanishes. Preliminary DFT calculations on the contact ion pair, [Ca(OH2)5Cl]+, confirm its existence in such hydrate melts. In aqueous solutions of Ca(NO3)2, NO3− penetrates the first hydration sphere and spectroscopic evidence of weak nitrato-complex formation could be detected. This is the first comprehensive report on the symmetric stretching vibration of the hydrated Ca2+ ion, [Ca(OH2)6]2+, in aqueous solution. DFT calculations concerning geometry optimizations and frequency calculations at the B3LYP/6-311+G(d,p) level on the hexa-aqua Ca2+ ion in the gas phase and including a solvation-sphere were performed. The calculations on [Ca(OH2)6]2+ and [Ca(OD2)6]2+ with a solvation-sphere allowed the determination of the six CaO6 skeletal modes and supported the assignment of the symmetric stretching mode, ν1CaO6 of [Ca(OH2)6]2+ and [Ca(OD2)6]2+. Discrete cluster calculations on a cluster with six inner sphere and twelve outer sphere water molecules, [Ca(OH2)6(OH2)12]2+ at the same level of theory, led to a Ca–O internuclear distance at 2.383 Å and 4.475 Å for the inner sphere and the outer sphere respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...