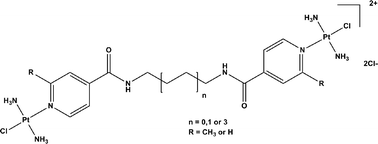
Picoplatin is a sterically hindered mononuclear platinum drug undergoing clinical trials. The 2-methylpyridine ring provides steric hindrance to the drug, preventing attack from biological nucleophiles. BBR3464 is a trinuclear platinum drug which was recently in Phase II clinical trials, and is highly cytotoxic both in vitro and in vivo; it derives this activity through the flexible adducts it forms with DNA. In this work we sought to combine the properties of both drugs to synthesise a family of sterically hindered, dinuclear platinum complexes as potential anticancer agents. The bis-pyridyl-based ligands were synthesised through a peptide coupling reaction using diaminoalkanes of differing lengths (n = 2, 4 or 8) and 4-carboxypyridine or 2-methyl-4-carboxypyridine. The resultant dinuclear platinum complexes were synthesised by reacting two equivalents of transplatin or mono-aquated transplatin to each ligand, followed by purification by precipitation with acetone. The unprotected complexes react faster with 5′-guanosine monophosphate (drug to nucleotide ratio 1 : 2; t1/2 = 2 h), glutathione (1 : 10, t1/2 = 55 min) and human serum albumin (HSA) (1 : 1, t1/2 = 24 h) compared to their hindered, protected equivalents (5′-guanosine monophosphate, t1/2 = 3.5 h; glutathione = 1.7 h; HSA, t1/2 = 110 h). The complexes were tested for in vitro cytotoxicity in the A2780 and A2780/cp70 ovarian cancer cell line. The unprotected platinum complexes were more cytotoxic than their protected derivatives, but none of the complexes were able to overcome resistance. The results provide important proof-of-concept for the development of a larger family of sterically hindered multinuclear-based platinum complexes.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...