A 3D α-Fe2O3 nanoflake urchin-like structure for electromagnetic wave absorption
Abstract
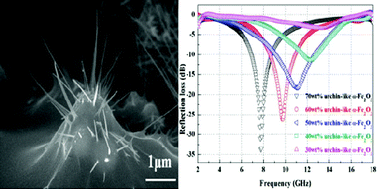
An α-Fe2O3 nanoflake urchin-like structure is formed via the thermal oxidation of micrometre-sized iron spheres in air at temperatures of 300–400 °C. The material consists of α-Fe2O3 nanoflakes grown perpendicularly to the sphere surface, a layer of a mixture of α-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 as the oxidation shell, and an iron core. The ranges of the tip diameters of the nanoflakes are 20–30 nm (300 °C), 30–50 nm (350 °C), and 60–100 nm (400 °C). A composite consisting of the α-Fe2O3 nanoflake urchin-like structure and an epoxy resin exhibits an excellent electromagnetic (

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...