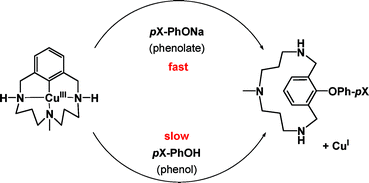
Aryl–O reductive elimination from reaction of well-defined aryl–Cuiii species with phenolates: the importance of ligand reactivity†
Abstract
Well-defined
- This article is part of the themed collection: Pincers and other hemilabile ligands

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...