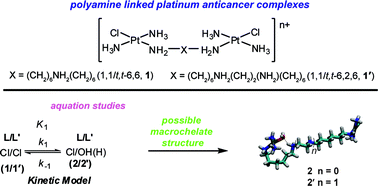
The aquation profiles of two novel dinuclear polyamine-linked, platinum-based antitumour complexes [{trans-PtCl(15NH3)2}2{μ-(15NH2(CH2)615NH2(CH2)615NH2)}]3+ (BBR3007, 1,1/t,t-6,6, 1) and [{trans-PtCl(15NH3)2}2{μ-(15NH2(CH2)615NH2(CH2)215NH2(CH2)615NH2)}]4+ (BBR3610, 1,1/t,t-6,2,6, 1′) have been probed using 2D [1H, 15N] HSQC NMR spectroscopy. Reported herein are the rate constants for the hydrolysis of 1 and 1′, as well as the acid dissociation constants of the coordinated aqua ligands in their aquated derivatives. The aquation and anation rate constants for the single step aquation model in 15 mM NaClO4 (pH 5.4) at 298 K are, for 1, k1 = 7.2 ± 0.1 ×10−5s−1, k−1 = 0.096 ± 0.002 M−1s−1 and, for 1′, k1 = 4.0 ± 0.2 × 10−5s−1, k−1 = 1.4 ± 0.1 M−1s−1. The effect of the linker backbone (Pt(tetra(m)mine vs.polyamine) was evaluated by comparison with previous data for the trinuclear complex [{trans-PtCl(NH3)2}2(μ-trans-Pt(NH3)2{NH2(CH2)6NH2}2)]4+ (1,0,1/t,t,t or BBR3464). The pK1 for 1,0,1/t,t,t (3.44) is closest to that of 1 (3.12), while the pronounced difference for 1′ (4.54), means that 1′ is the least aquated of the three complexes at equilibrium. pKa values of 5.92 were calculated for the aquated forms of both 1 and 1′, which are 0.3 pK units higher than for either 1,0,1/t,t,t, or the dinuclear 1,1/t,t. The higher pKa values for both polyamine-linked compounds may be attributed to the formation of macrochelates between the central NH2 groups and the {PtN3O} coordination sphere of the aquated species.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...