Carboxyl-functionalized nanoparticles with magnetic core and mesopore carbon shell as adsorbents for the removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution†
Abstract
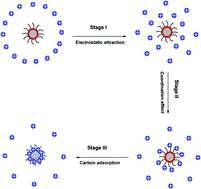
This communication demonstrates superparamagnetic nanosized particles with a magnetic core and a porous carbon shell (thickness of 11 nm), which can remove 97% of Pb2+ ions from an acidic aqueous solution at a Pb2+ ion concentration of 100 mg L−1. It is suggested that a weak electrostatic force of attraction between the heavy metal ions and the

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...