The reactivities of [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]AlH2 (1) with primary and secondary amines, phenols, ketones, and phenyl isothiocyanate were examined. Reactions of 1 with one or two equivalents of 2,6-dichloroaniline in methylene chloride generated [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]AlH(NHC6H3-2,6-Cl2) (2) and [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]Al(NHC6H3-2,6-Cl2)2 (3), respectively, following hydrogen elimination. Similarly, the reactions of 1 with one or two equivalents of carbazole afforded [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]AlH(NC12H8) (4) or [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]Al(NC12H8)2 (5) by deprotonating the acidic N–H of carbazole. Reacting 1 with one equivalent of 2,6-diisopropylphenol in diethyl ether formed an aluminium phenoxo compound [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]AlH(OC6H3-2,6-iPr2) (6), by deprotonation of phenol as well with the elimination of one equivalent hydrogen. Further reaction of 6 with one equivalent of 2,4,6-trimethylacetophenone in methylene chloride generated [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]Al(OC6H3-2,6-iPr2)[OC(![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2)(C6H2-2,4,6-Me3)] (7) by deprotonating the methyl proton of the acetophenone. Similar deprotonation occurred when 1 reacted with two equivalents of 2,4,6-trimethylacetophenone in methylene chloride to generate [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]Al[OC(
CH2)(C6H2-2,4,6-Me3)] (7) by deprotonating the methyl proton of the acetophenone. Similar deprotonation occurred when 1 reacted with two equivalents of 2,4,6-trimethylacetophenone in methylene chloride to generate [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]Al[OC(![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2)(C6H2-2,4,6-Me3)]2 (8). Compounds [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]Al(OCHPh2)2 (9), and [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]Al(SCHNPh)2 (10) could also be obtained by reacting 1 with two equivalents of benzophenone and phenyl isothiocyanate, respectively through hydroalumination. The 1H NMR spectra of 10 showed broad signals for the CH2N and NMe2 groups, which represent dynamical fluctuations of the molecules in solution state. The estimated energy barrier (ΔGc‡) from the coalescence temperature for the fluctuation was estimated at 17.1 Kcal mol−1. The solid-state structures of compounds 2, 3, 5, 7, 9, and 10 have been determined.
CH2)(C6H2-2,4,6-Me3)]2 (8). Compounds [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]Al(OCHPh2)2 (9), and [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]Al(SCHNPh)2 (10) could also be obtained by reacting 1 with two equivalents of benzophenone and phenyl isothiocyanate, respectively through hydroalumination. The 1H NMR spectra of 10 showed broad signals for the CH2N and NMe2 groups, which represent dynamical fluctuations of the molecules in solution state. The estimated energy barrier (ΔGc‡) from the coalescence temperature for the fluctuation was estimated at 17.1 Kcal mol−1. The solid-state structures of compounds 2, 3, 5, 7, 9, and 10 have been determined.
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2)(C6H2-2,4,6-Me3)] (7) by deprotonating the
CH2)(C6H2-2,4,6-Me3)] (7) by deprotonating the ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2)(C6H2-2,4,6-Me3)]2 (8). Compounds [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]Al(OCHPh2)2 (9), and [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]Al(SCHNPh)2 (10) could also be obtained by reacting 1 with two equivalents of
CH2)(C6H2-2,4,6-Me3)]2 (8). Compounds [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]Al(OCHPh2)2 (9), and [C4H2N(CH2NMe2)2]Al(SCHNPh)2 (10) could also be obtained by reacting 1 with two equivalents of 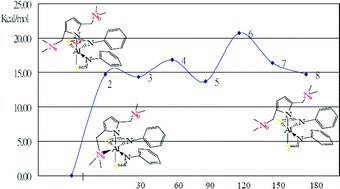

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...