The dinuclear bis-iminosemiquinonato [Ru(bpy)2(L)2Ru(bpy)2](PF6)2 complex where L is the deprotonated form of N,N′-bis(3,5-di-tert-butyl-2-hydroxyphenyl)-1,3-phenylenediamine (H4L), has been synthesised. For comparison purposes, the mononuclear iminosemiquinonato [Ru(bpy)2L′]PF6 formed by the N-phenyl-o-aminophenol (H2L′) was also investigated. Magnetic investigation evidences that the bis-semiquinonato species is characterised by a moderately strong ferromagnetic interaction (H
=
JS1·S2, J
=
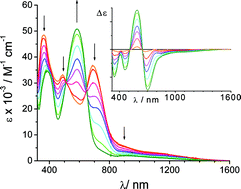
−85(5) cm−1). This result is the theoretically expected one and it is contrasting with the antiferromagnetic interaction observed in previously investigated complexes containing the same ligand. It is suggested that the different behaviour is determined by the different coordination requirements occurring in these complexes. The spectroelectrochemical analysis provides a clear evidence of the valence trapped character of the mono-semiquinonato forms of the ligand. The two mixed valence semiquinonato species containing the quinonato-semiquinonato and semiquinonato-catecholato bridging ligand can be described as class II, but show a significantly different electronic coupling. The electronic factors determining this behaviour are discussed.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...