Probing the aqueous copper(ii) coordination chemistry of bifunctional chelating amino acid ligands with a luminescent ruthenium chromophore
Abstract
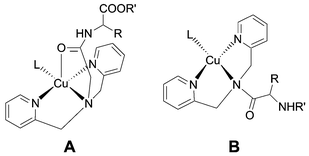
A covalently attached fluorescent [Ru(bipy)3]2+ label was used to probe the coordination chemistry of two different bpa–amino acid (bpa = bis(2-picolyl)amine) conjugates with copper(II) ions in aqueous solutions. The ligand moiety bpaAc–AA (Ac = acyl) is quadridentate and contains an O-coordinating secondary amide function. It forms a stable 1:1 complex with Cu2+ ions in a pH range between 2 and 12. This is evident from an efficient quenching of the ruthenium based emission. The Cu+/2+ redox transition is reversible. Formation of the copper(I) complex results in a restoration of the luminescence intensity. It is thereby possible to switch the emission ON and OFF by chemical reduction and oxidation with hydrazine and hydrogen peroxide, respectively. The ligand framework AA–bpa is tridentate and contains a tertiary carboxamide linkage. This functional group causes a dramatically lower affinity for copper(II) ions. A complex is only formed in a pH range between 8 and 10. The formation is slow and results in a subsequent cleavage of the tertiary amide bond. Implications for the use of both ligand moieties for the design of bioinorganic hybrid molecules are discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...