Following palladium catalyzed methoxycarbonylation by hyperpolarized NMR spectroscopy: a parahydrogen based investigation†
Abstract
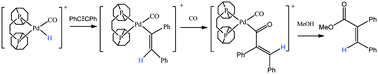
Pd(OTf)2(bcope) is shown to react in methanol solution with diphenylacetylene, carbon monoxide and hydrogen to produce the methoxy-carbonylation product methyl 2,3 diphenyl acrylate alongside cis- and trans-stilbene. In situ NMR studies harnessing the parahydrogen induced polarization effect reveal substantially enhanced 1H NMR signals in both protic and aprotic solvents for a series of reaction intermediates that play a direct role in this homogeneous transformation. Exchange spectroscopy (EXSY) measurements reveal that the corresponding CO adducts are less reactive than their methanol counterparts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...