Highly efficient removal of organic contaminants based on peroxymonosulfate activation by iron phthalocyanine: mechanism and the bicarbonate ion enhancement effect†
Abstract
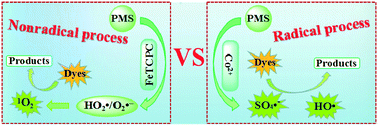
The development of catalytic oxidation processes with high efficiency based on peroxymonosulfate (PMS) activation is a promising yet challenging research topic in the environmental catalysis field. In this work, iron tetracarboxyphthalocyanine (FeTCPc) as a homogeneous catalyst is proposed for PMS activation and construction of a novel and efficient catalytic system for the removal of Acid Orange 7 (AO7). In this system, FeTCPc exhibited extra-high catalytic activity for PMS activation, even higher than the Co2+ analogue of the catalyst which was identified as one of the most efficient PMS activators. A hybrid method that combines electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) technology with different radical scavengers was employed for the investigation of active species, and the results indicate that superoxide radicals (HO2˙/O2˙−) and singlet oxygen (1O2) other than the sulfate radical (SO4˙−) or hydroxyl radical (HO˙) were the primary reactive oxygen species during the catalytic oxidation process. Moreover, this system turned the negative effect of HCO3− observed in most reported Co2+/PMS systems into a positive one, which accelerated the AO7 removal with an over 10-fold increase of the rate constant due to generation of more 1O2. This study reports on a novel catalytic oxidation pathway for PMS activation, and paves an avenue toward developing highly efficient catalytic oxidation processes for the treatment of organic contaminants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...