Support morphology and crystal plane effect of Cu/CeO2 nanomaterial on the physicochemical and catalytic properties for carbonate hydrogenation†
Abstract
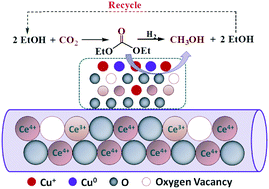
The present work determined the morphology and crystal plane effects of nanoceria on the activity of Cu/CeO2 catalysts in the gas/solid-phase hydrogenation of CO2-derived diethyl carbonate (DEC) to methanol. The effect of the terminating crystalline planes of CeO2 ({100}, {110}, and {111}) on the behaviour of copper species dispersed over CeO2 nanocubes, nanorods and nanoparticles was examined in detail using a variety of characterization techniques. HRTEM studies revealed that CeO2 nanorods were mainly enclosed by {100} and {110} planes, nanoparticles exhibited only {111} surfaces, and nanocubes predominantly displayed {100} planes. Cu/CeO2 nanorods (Cu/Ce-NR) possessed higher Cu+/Cu0 ratios and more oxygen vacancies than Cu/CeO2 nanoparticles (Cu/Ce-NP) and Cu/CeO2 nanocubes (Cu/Ce-NC), which indicated that there was a stronger interaction between Cu and CeO2 nanorods. A test of activity in the hydrogenation of DEC showed that Cu/Ce-NR was more active than Cu/Ce-NP and Cu/Ce-NC, which could be attributed to the higher value of SCu0, surface oxygen mobility and Cu+/Cu0 ratio. These results confirm that the activity of Cu/CeO2 catalysts for the hydrogenation of DEC is greatly affected by the shape/crystal planes of CeO2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...