Direct conversion of formaldehyde to ethylene glycol via photocatalytic carbon–carbon coupling over bismuth vanadate†
Abstract
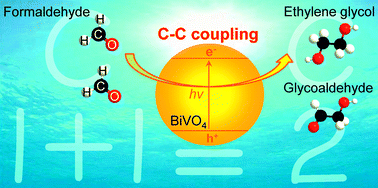
We report a novel and direct conversion of formaldehyde into C2 compounds, in particular ethylene glycol, via photocatalytic carbon–carbon coupling over BiVO4, a visible-light-responsive and robust semiconductor. The generation of V4+ on BiVO4 surfaces enhanced the photocatalytic formation of C2 compounds.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...