A study on the origin of the active sites of HDN catalysts using alumina-supported MoS3 nanoparticles as a precursor†
Abstract
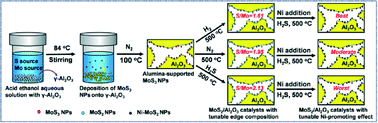
This article proposes alumina-supported MoS3 nanoparticles (NPs) as a precursor of model catalysts to study hydrodenitrogenation (HDN) catalytic mechanisms. The NPs were first loaded into γ-Al2O3 by a simple chemical deposition method and then thermally treated under H2, N2 and H2S atmospheres, respectively, to obtain three MoS2/Al2O3 catalysts. The XPS, N2 adsorption–desorption and HRTEM characterization results show that using MoS3 NPs instead of conventional MoOx NPs as the precursor can effectively tune the edge composition of the MoS2 phase while controlling its micromorphology and avoiding the strong interference from the alumina support to the phase, thus laying the foundation for accurate understanding of the origin of the active sites for HDN reactions. Then the catalytic activity of a series of MoS3-derived catalysts was thoroughly studied and comprehensive results are obtained after rationally deducing the “structure–function” relations: (i) two types of active sites exist in the HDN catalysts, one for the hydrogenation reaction which is related to both sulfur vacancies and brim sites and another for the C–N hydrogenolysis reaction which is connected with the –SH/S2− groups on the edge of the active phase; (ii) the edge composition directly influences the Ni-promoting effect and the “sulfur-deficient” edge structure is more beneficial for the promoter role of Ni. Due to the actual catalyst model first used, the resulting viewpoints exhibit valuable guiding significance for highly efficient HDN catalyst development.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...