Rapid degradation of oxidation resistant nitrophenols by TAML activator and H2O2†
Abstract
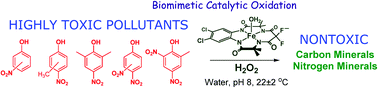
Nitrophenols (NPs) are widely prevalent recalcitrant anthropogenic pollutants. TAML activators in conjunction with peroxides have proven to be effective in the remediation of myriad organic pollutants. In the present study, we have discovered that one of the most reactive TAML activators 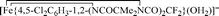 (1) catalyses the oxidative degradation by H2O2 of mono- and dinitrophenols (including all US-EPA classified priority pollutants) under ambient conditions at pH 8 which is close to pH of environmental waters. Individual nitrophenols as well as mixtures thereof undergo fast decontamination (reaction time ≤45 min) resulting in deep oxidation producing HCO2− and minerals, CO, CO2, NO2−, and NO3− (up to 99% of N and 70% of C). The remarkable efficacy of the 1/H2O2-mediated decontamination process is matched by complete elimination of the toxicity of the nitrophenols (Microtox® assays). Detailed mechanistic studies of the catalyzed oxidation revealed a strong substrate inhibition of the catalytic activity for some nitrophenols, the strongest being observed for 4-nitrophenol. DFT calculations suggest that the inhibition is likely due to reversible binding of nitrophenolate anions to the iron(III) center of the resting state of the 1 catalyst, which compromises its reactivity toward H2O2.
(1) catalyses the oxidative degradation by H2O2 of mono- and dinitrophenols (including all US-EPA classified priority pollutants) under ambient conditions at pH 8 which is close to pH of environmental waters. Individual nitrophenols as well as mixtures thereof undergo fast decontamination (reaction time ≤45 min) resulting in deep oxidation producing HCO2− and minerals, CO, CO2, NO2−, and NO3− (up to 99% of N and 70% of C). The remarkable efficacy of the 1/H2O2-mediated decontamination process is matched by complete elimination of the toxicity of the nitrophenols (Microtox® assays). Detailed mechanistic studies of the catalyzed oxidation revealed a strong substrate inhibition of the catalytic activity for some nitrophenols, the strongest being observed for 4-nitrophenol. DFT calculations suggest that the inhibition is likely due to reversible binding of nitrophenolate anions to the iron(III) center of the resting state of the 1 catalyst, which compromises its reactivity toward H2O2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...