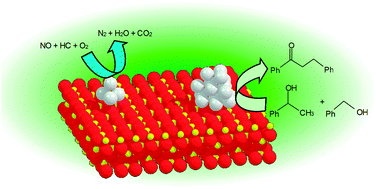
The size control of Ag into nanoclusters generates unique catalytic features of Ag on automotive emission control and environmentally friendly organic reactions. Hydrogen-assisted selective catalytic reduction of NO by hydrocarbons (H2–HC–SCR), which is one of the promising technologies for removal of NO in the diesel engine exhausts, results in the formation of Ag clusters on alumina or zeolites and enhancement of the conversion of NO into N2. A mechanistic study using in situUV-Vis, EXAFS, and FT/IR revealed that the promotion of partial oxidation of hydrocarbons by active oxygen species is the essential role of Ag clusters. Hydrogen is suggested to be indispensable for the formation of the Ag cluster and the active oxygen. The important role of hydride on the formation of H2O2-like active chemical species on Ag clusters was confirmed by density functional theory (DFT) calculation. Knowing the high activity of Ag nanoclusters for the formation of Ag-hydride, supported Ag clusters were applied for various organic reactions. Supported Ag clusters on appropriate metal oxide, especially Al2O3, are recyclable and show very high activity and selectivity for atom-economic reactions, i.e., alcohol dehydrogenation, C–C coupling reaction of alcohols, direct amide synthesis from alcohols and amines, N-benzylation of anilines with alcohols, and selective hydrogenation of nitroaromatics.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...