Enantioselective C–C bond synthesis catalysed by enzymes
Abstract
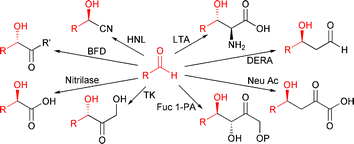
The enantioselective synthesis of C–C bonds is often the pivotal step of a synthesis. Nature has made a variety of versatile enzymes available that catalyse this type of reaction very selectively under mild conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...