Dynamic micellar oligomers of amyloid beta peptides play a crucial role in their aggregation mechanisms†
Abstract
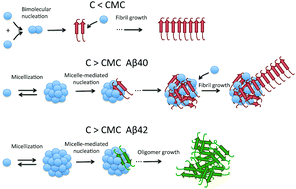
A deep understanding of the early molecular mechanism of amyloid beta peptides (Aβ) is crucial to develop therapeutic and preventive approaches for Alzheimer's disease (AD). Using a variety of biophysical techniques, we have found that micelle-like dynamic oligomers are rapidly formed by Aβ40 and Aβ42 above specific critical concentrations. Analysis of the initial aggregation rates at 37 °C measured by thioflavin T and Bis-ANS fluorescence using a mass-action micellization model revealed a concentration-dependent switch in the nucleation mechanism. Bimolecular nucleation appears to occur at low peptide concentration while above the critical micellar concentration, the nucleation takes place more efficiently in the micelles. Upon incubation, these micelles mediate a rapid formation of larger, more stable oligomers enriched in beta-sheet structure. These oligomers formed from Aβ40, enriched in amyloid nuclei, acquire a higher capacity to fibrillate than their micellar precursors. Aβ42 can also form similar oligomers but they have lower beta-sheet structure content and lower capacity to fibrillate. On the other hand, a considerable fraction of the Aβ42 peptide forms morphologically distinct oligomers that are unable to fibrillate and show significant effect on SH-SY5Y cell viability. Overall, our results highlight the importance of micellar structures as mediators of amyloid nucleation and contribute to the understanding of the differences between the aggregation pathways of Aβ40 and Aβ42.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...