Ammonolysis of ketene as a potential source of acetamide in the troposphere: a quantum chemical investigation†
Abstract
Quantum chemical calculations at the CCSD(T)/CBS//MP2/aug-cc-pVTZ levels of theory have been carried out to investigate a potential new source of acetamide in Earth's atmosphere through the ammonolysis of the simplest ketene. It was found that the reaction can occur via the addition of ammonia at either the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C or C
C or C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond of ketene. The potential energy surface as well as calculated rate coefficients indicate that under tropospheric conditions, ammonolysis would occur almost exclusively via ammonia addition at the C
O bond of ketene. The potential energy surface as well as calculated rate coefficients indicate that under tropospheric conditions, ammonolysis would occur almost exclusively via ammonia addition at the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond with negligible contribution from addition at the C
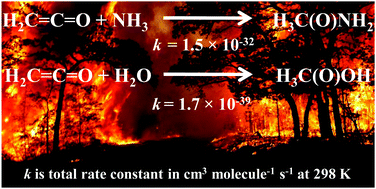
O bond with negligible contribution from addition at the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond. The reaction of ketene with water has also been investigated in order to compare between hydrolysis and ammonolysis, as the former is known to be responsible for the formation of acetic acid. The rate coefficient for the formation of acetamide was found to be ∼106 to 109 times higher than that for the formation of acetic acid from the same ketene source in the troposphere. By means of the relative rate of ammonolysis with respect to hydrolysis, it was shown that acetamide formation would dominate over acetic acid formation at various altitudes in the troposphere.
C bond. The reaction of ketene with water has also been investigated in order to compare between hydrolysis and ammonolysis, as the former is known to be responsible for the formation of acetic acid. The rate coefficient for the formation of acetamide was found to be ∼106 to 109 times higher than that for the formation of acetic acid from the same ketene source in the troposphere. By means of the relative rate of ammonolysis with respect to hydrolysis, it was shown that acetamide formation would dominate over acetic acid formation at various altitudes in the troposphere.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...