Monitoring the chemical and electronic properties of electrolyte–electrode interfaces in all-solid-state batteries using operando X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy†
Abstract
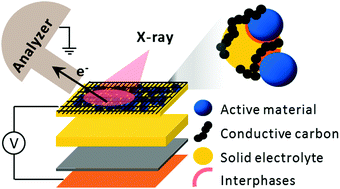
Understanding the degradation of the solid electrolyte–electrodes interface during cycling is currently one of the most challenging obstacles in the development of all-solid-state batteries. Here, we introduce operando X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) as a combined approach for real-time monitoring of the (i) (electro-) chemical interfacial reactions between different components of the composites electrode and (ii) surface electronic properties. The dedicated electrochemical cell, capable of maintaining high mechanical pressure, offers reliable electrochemistry and versatility in terms of materials application. We propose a fundamental physical model to explain the effect of applied cell voltage on core level binding energy shifts, which allows direct contactless measurement of the surface potentials. Such a fundamental understanding is also an essential prerequisite for (i) accurate interpretation of the XPS core level peaks, (ii) the assignment of solid electrolyte decomposition byproducts and (iii) an improved description of the interfacial reaction mechanisms in all-solid-state batteries. A mixture of LiCoO2 (LCO) and (Li2S)3–P2S5 (LPS) cycled vs. InLix is investigated revealing that the LPS oxidation begins above 2.1 V vs. InLix and the byproducts passivate the composite surface against further oxidation. Moreover, we confirm that LCO particles are electronically conductive even in the absence of conductive additives by measuring directly its surface potential during cycling.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...